5G Satellite (NTN)

MediaTek’s Vision for Satellite Connectivity
MediaTek believes that integrating satellite and terrestrial mobile networks in a single device offers pervasive global connectivity. It will not only enable a new era of innovative digital services, but also further democratize global connectivity, giving more people than ever before access to the internet.
MediaTek is promoting satellite connectivity based on global, open standards that can leverage the economies of scale from the existing global mobile cellular ecosystem, bringing satellite communication from a niche market to mainstream consumers and businesses in devices that can seamlessly switch between satellite and cellular networks to provide an always connected experience.
What is 5G Satellite Connectivity, or “NTN”?
Satellite connectivity is called a Non-Terrestrial Network, or NTN. NTN technology enables data connectivity beyond terrestrial cellular tower coverage (TN), allowing users to always be connected. NTN is ready to fill gaps in terrestrial cellular coverage with data rates that lets users send messages, receive emergency alerts, location data, and will eventually allow real-time voice and video calls, and seamless experiences in smartphone apps.
Users might find themselves beyond TN coverage in a remote location, or due to infrastructure damage caused by natural disasters. In such situations, NTN provides essential services like emergency communication and navigation.
While satellite phones have been available for quite some time, these are currently specialized, proprietary devices that operate exclusively outside of regular cellular networks. With 3GPP standards-based NTN that MediaTek is promoting, everyone who owns a regular 5G smartphone will eventually have access to satellite communication.
5G NTN Includes Two Connectivity Standards
IoT-NTN
Designed for low data-rate connections such as messaging or non-realtime data exchange in agriculture, forestry, logistics, transportation, and other industries that operate in remote areas outside of terrestrial cellular coverage.
NR-NTN
Designed for higher data-rate connections that enable services such as voice and video calls, sending photos and short videos, and basic media streaming experiences.
World’s First Commercially Available 5G NTN Chipset
MediaTek MT6825
The MediaTek MT6825 is the world’s first commercially available 5G IoT-NTN chipset. It can connect to Geosynchronous Equatorial Orbit (GEO) constellations, which can be converted into 3GPP NTN compliant network easily and are widely available now on the orbit. To provide a seamless experience, MT6825 allows devices to automatically receive messages from satellites, unlike competitive solutions that currently require users to manually check for messages. The highly integrated chipset design accelerates time to market and affords excellent power efficiency to extend device battery life as much as possible.
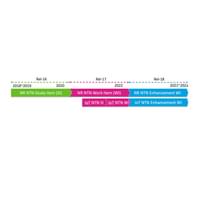
MediaTek is the Proponent and Project Leader of 3GPP NTN Standardization
By driving the creation of and advocating for 5G NTN products and ecosystem that adheres to 3GPP standards, MediaTek is leading the way towards global interoperability and accessibility among cellular services worldwide, benefitting users and industries in a wide range of cellular devices.
Industry Leadership Timeline
2019
December 2019: MediaTek’s IoT-NTN study proposal approved by 3GPP.
2020
August 2020: MediaTek conducts the world’s first public test of an IoT-NTN data connection. Read More
2021
June 2021: On MediaTek’s proposal, 3GPP agree to accelerate IoT-NTN standardization.
2022
August 2022: MediaTek demonstrates the world’s first successful test of 5G NR-NTN connectivity. Read More
December 2022: The first standards-based IoT-NTN chip – MediaTek MT6825 – is featured in the first 5G smartphone. Read More
2023
March 2023: MediaTek Showcases the world’s first live demonstration of NR-NTN connection using an upcoming MediaTek 5G modem. Read More >
March 2023: Motorola announces its Defy 2, rugged 5G NTN smartphone and Defy Satellite Link.
Further Reading
- IEEE: Satellite and Terrestrial Network Convergence on the Way toward 6G
- MediaTek 6G Technology White Paper - Satellite and Terrestrial Network Convergence (coming soon)
